Hi Folks,
Model Context Protocol(MCP) has quickly become one of the hottest topics in today’s AI landscape. The excitement around it is huge—not just within the Microsoft ecosystem, but across the entire industry, because it’s designed to be open and accessible to everyone.
Microsoft Power Platform is also moving fast, releasing its own MCPs. I’ve already been asked several times about the difference between them, so this post breaks down how the Dataverse MCP and the Power Apps MCP differ—and when you should use each one.
We know that Dataverse MCP is generally available last year. Now Microsoft announced the public preview of Power Apps MCP this month. So what’s the difference between the two, this post will help to discern the differences between two.
Although both use the Model Context Protocol (MCP), they serve different purposes and operate at different layers of the Power Platform.
| Feature | Dataverse MCP | Power Apps MCP |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Expose Dataverse as an MCP server so AI agents can query tables, records, and metadata | Allow Power Apps to use MCP to call external AI models or tools |
| Focus | Data access & operations | AI integration inside apps |
| Who Uses It | Developers building AI agents or copilots that need Dataverse data | App makers building Power Apps that need AI-driven logic |
2. Direction of Integration
| Direction | Dataverse MCP | Power Apps MCP |
|---|---|---|
| MCP Server | Yes — Dataverse acts as an MCP server | No |
| MCP Client | No | Yes — Power Apps acts as an MCP client |
| Meaning | AI tools connect into Dataverse | Power Apps connects out to AI tools |
Dataverse MCP: AI → Dataverse Power Apps MCP: Power Apps → AI
3. What You Can Do
Dataverse MCP
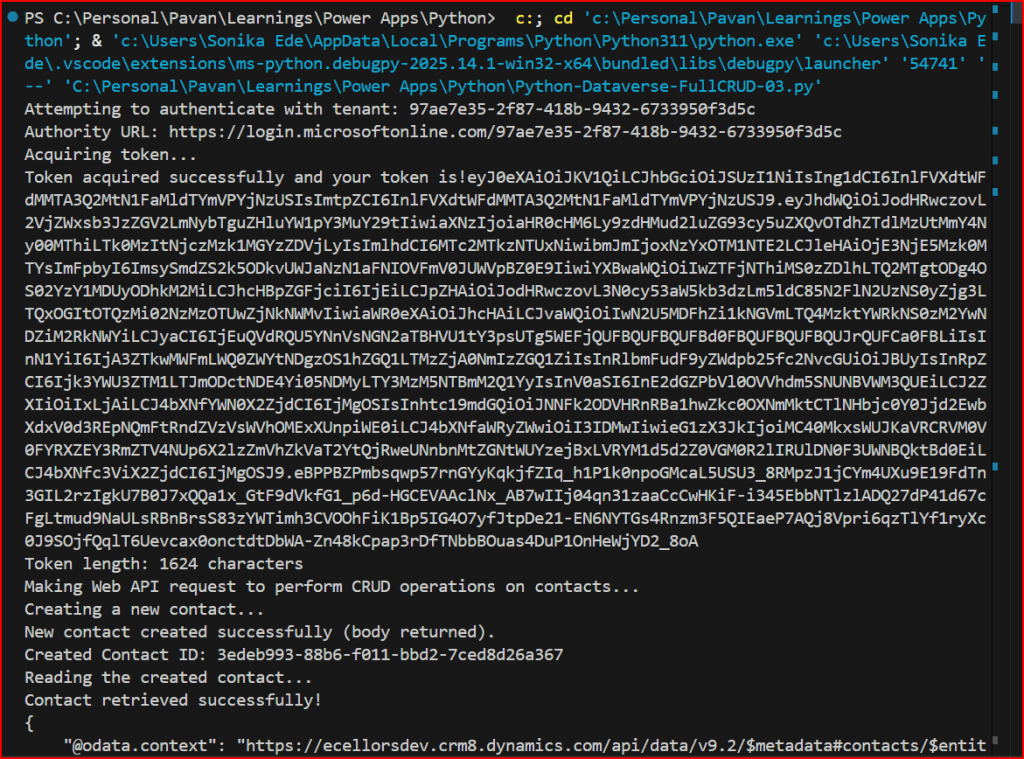
- Query Dataverse tables
- Retrieve records
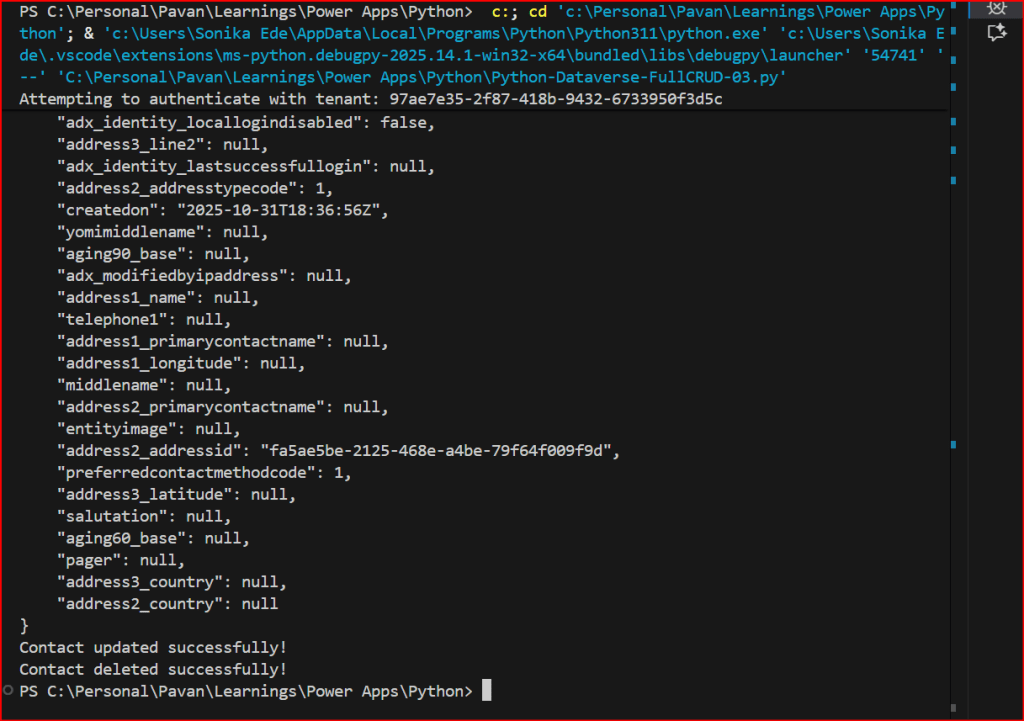
- Update or create data
- Use Dataverse as a tool inside Copilot Studio, VS Code GitHub Copilot, Claude Desktop, etc.
Power Apps MCP
- Call external AI models from inside a Power App
- Build AI-driven app logic
- Trigger workflows using AI reasoning
4. Typical Use Cases
Dataverse MCP
- Build a Copilot that answers questions using Dataverse data
- Let GitHub Copilot query Dataverse while coding
- Create AI agents that read/write CRM or ERP data
Power Apps MCP
- Add AI reasoning to a canvas or model-driven app
- Use external AI models to classify, summarize, or generate content
- Build intelligent forms or workflows
5. Relation to Connectors
Dataverse MCP is increasingly seen as a future alternative to connectors for AI-driven scenarios.
Power Apps MCP does not replace connectors — it extends apps with AI capabilities.
Summary
| Category | Dataverse MCP | Power Apps MCP |
|---|---|---|
| Acts as | MCP Server | MCP Client |
| Used for | AI agents accessing Dataverse | Power Apps calling AI tools |
| Primary Benefit | Intelligent, standardized Dataverse access | AI-enhanced app logic |
| Typical Tools | Copilot Studio, GitHub Copilot, Claude | Canvas apps, model-driven apps |
Decision Guide: When to Use Dataverse MCP vs Power Apps MCP
1. If you want AI to access Dataverse → Use Dataverse MCP
Choose Dataverse MCP when:
- You’re building a Copilot, AI agent, or LLM-powered tool that needs:
- Dataverse tables
- Records
- Metadata
- CRUD operations
- You want AI to reason over business data
- You want a standardized, connector-free way for AI to talk to Dataverse
- You’re integrating Dataverse with:
- GitHub Copilot
- Copilot Studio
- Claude Desktop
- Custom LLM agents
Typical scenarios
- My AI assistant should answer questions using CRM data.
- I want GitHub Copilot to autocomplete code based on Dataverse schema.
- I’m building an AI agent that updates Dataverse records.
If the AI is the one doing the work → Dataverse MCP.
2. If you want your Power App to call AI → Use Power Apps MCP
Choose Power Apps MCP when:
- You’re building a canvas or model-driven app that needs:
- AI reasoning
- AI-generated content
- AI classification or summarization
- You want your app to call:
- OpenAI models
- Azure AI models
- Custom MCP tools
- You want AI logic inside the app, not outside it
Typical scenarios
- My form should summarize customer notes using AI.
- My app should classify images or text using an external model.
- I want to call an LLM from a button in a canvas app.
3. If you need both directions → Use both
Some solutions need AI ↔ Dataverse ↔ Power Apps.
Example
- A Power App collects data
- AI agent (via Dataverse MCP) analyzes historical records
- Power App (via Power Apps MCP) calls AI to generate insights for the user
This is becoming a common pattern in enterprise AI.
4. Quick Decision Table
| Goal | Use Dataverse MCP | Use Power Apps MCP |
|---|---|---|
| AI needs to read/write Dataverse | ✅ | ❌ |
| Power App needs to call AI | ❌ | ✅ |
| Replace connectors for AI-driven data access | ✅ | ❌ |
| Add AI reasoning inside app UI | ❌ | ✅ |
| Build AI copilots or agents | ✅ | ❌ |
| Build AI-enhanced business apps | ❌ | ✅ |
Hope you have found this post useful….
Cheers,
PMDY