Hi Folks,
Do you know that you can connect to your Dataverse DB right from your old toolbox SSMS, an express version would be more than enough to try out. Possibly we didn’t think of, but yes, we can…so let’s see that in this blog post.
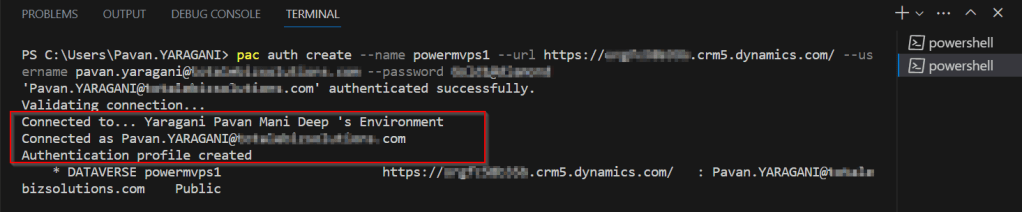
Open SSMS..
1.Select Server type as Database Engine

2. Server name as the environment URL from your Power Platform Admin Center as below.

3. So key in those details as below, make sure to Select Authentication method as Azure Active Directory – Universal with MFA option.
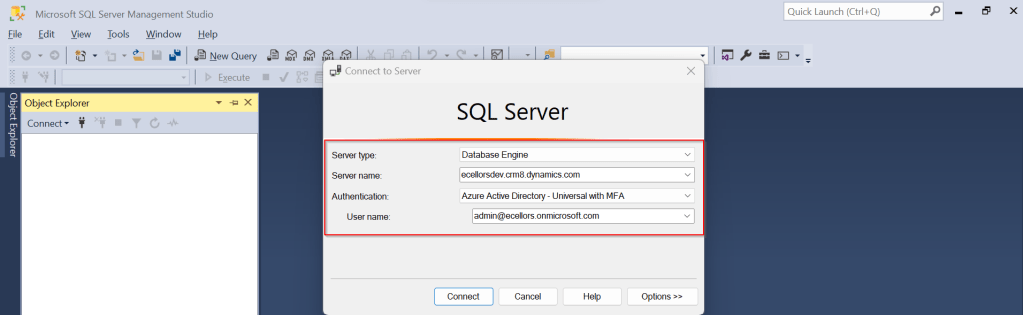
Once you click on Connect, you will be prompted for authentication via browser.
Once your Sign-In is successful, you will be able to see.

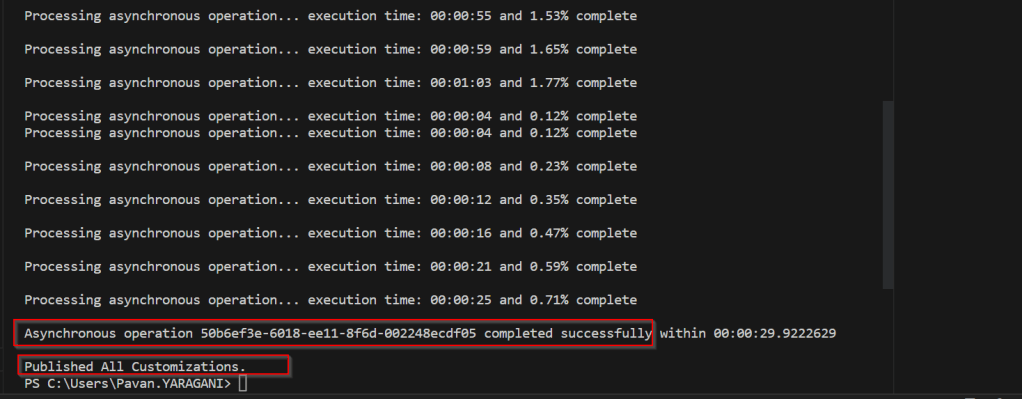
That’s it, how simple it was connecting to your Dataverse instances…
Having said that it’s easy to connect to Dataverse, not all operations performed using normal transact SQL are supported here using Dataverse SQL. You could see it says Read-Only besides the instance name, that means that you don’t have any capabilities to modify from SQL.
Because Dataverse SQL is a subset of Transact-SQL. If you want to see what statements are supported and what not, just go ahead to this link to find out.
This opens a whole lot of opportunities to explore, so don’t forget to check this out.
References:
Dataverse SQL and Transact SQL
Cheers,
PMDY